3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing method which is used to create an object by adding layers. The advantage of 3D printing – compared to other subtractive production methods – is that the use of resources is limited to the actually needed amount of material with only minimal waste.
Stereolithography
Stereolithography is a 3D printing method using photopolymerization to convert liquid plastic into solid 3D objects. Basically, liquid photosensitive resins are cured by a UV light source layer by layer. The addition of all these layers leads to the formation of the 3D object.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Digital Light Processing is a similar process to stereolithography, based on the idea of using photopolymers. However, the major difference is the light source which is applied to the entire bottom of the vat filled with photopolymer resin in a single pass, generally leading to faster printing speeds. At the same time, DLP produces highly accurate parts with excellent resolution. Also, the vat is more shallow which results in even less wasted material und a more economical production.
Digital Workflow
A typical digital workflow includes the following steps:
3D-Model
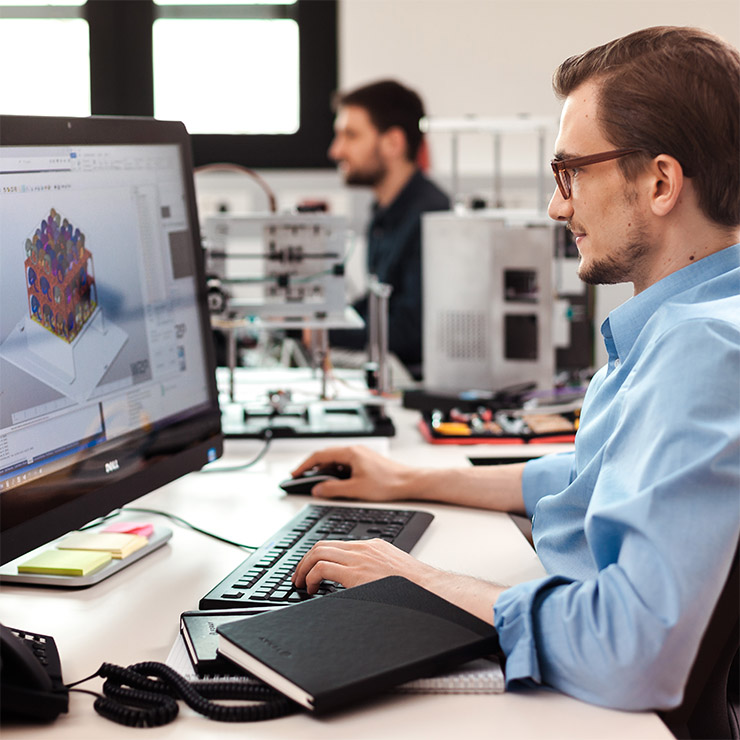
3D prints are based on 3D models which can be generated by taking a 3D scan or creating them in a CAD program.
3D-Software
Using a 3D print software, 3D models can be edited and made ready for printing by placing parts, modeling, building support structures and slicing.
Printing Process
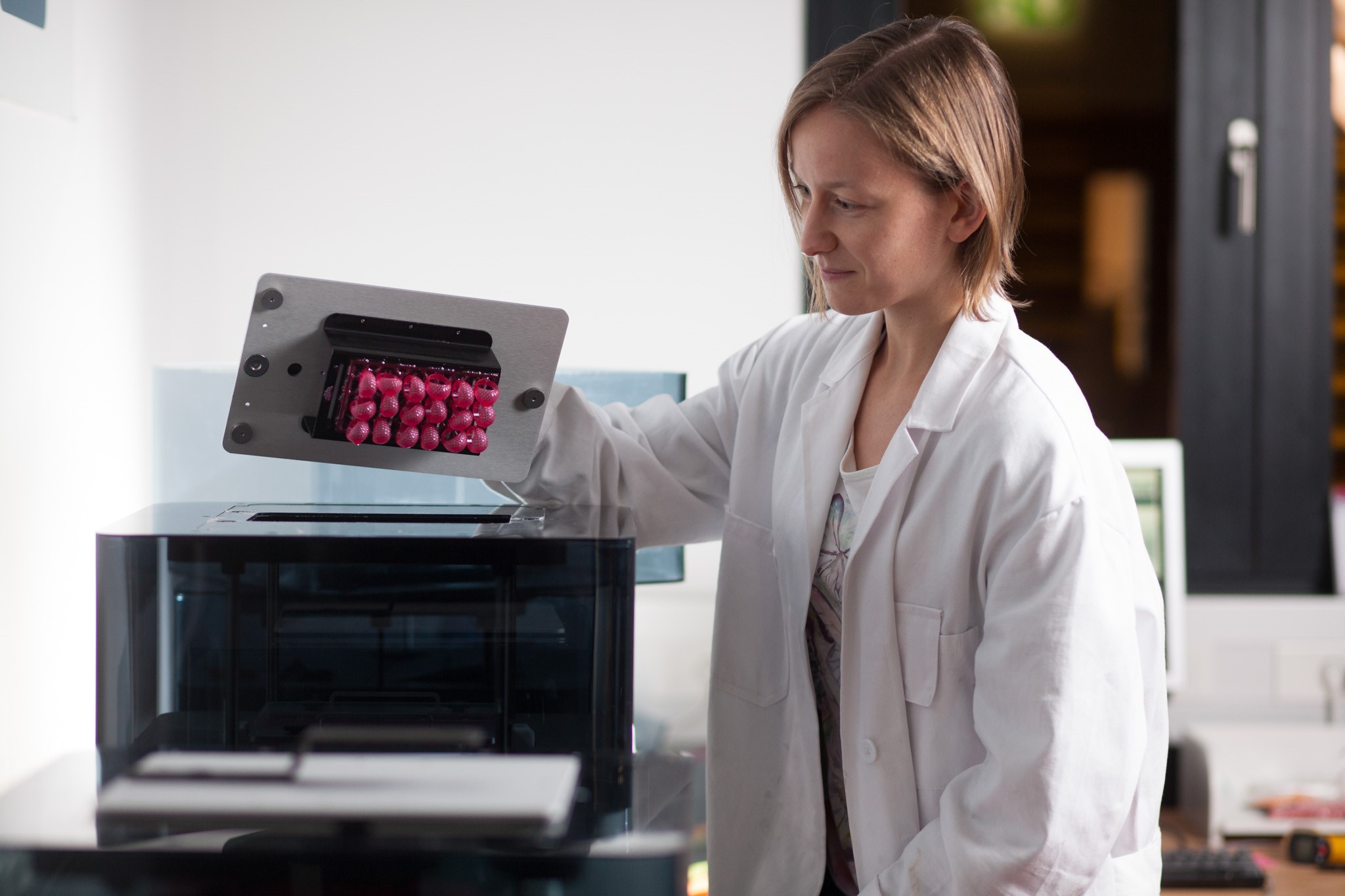
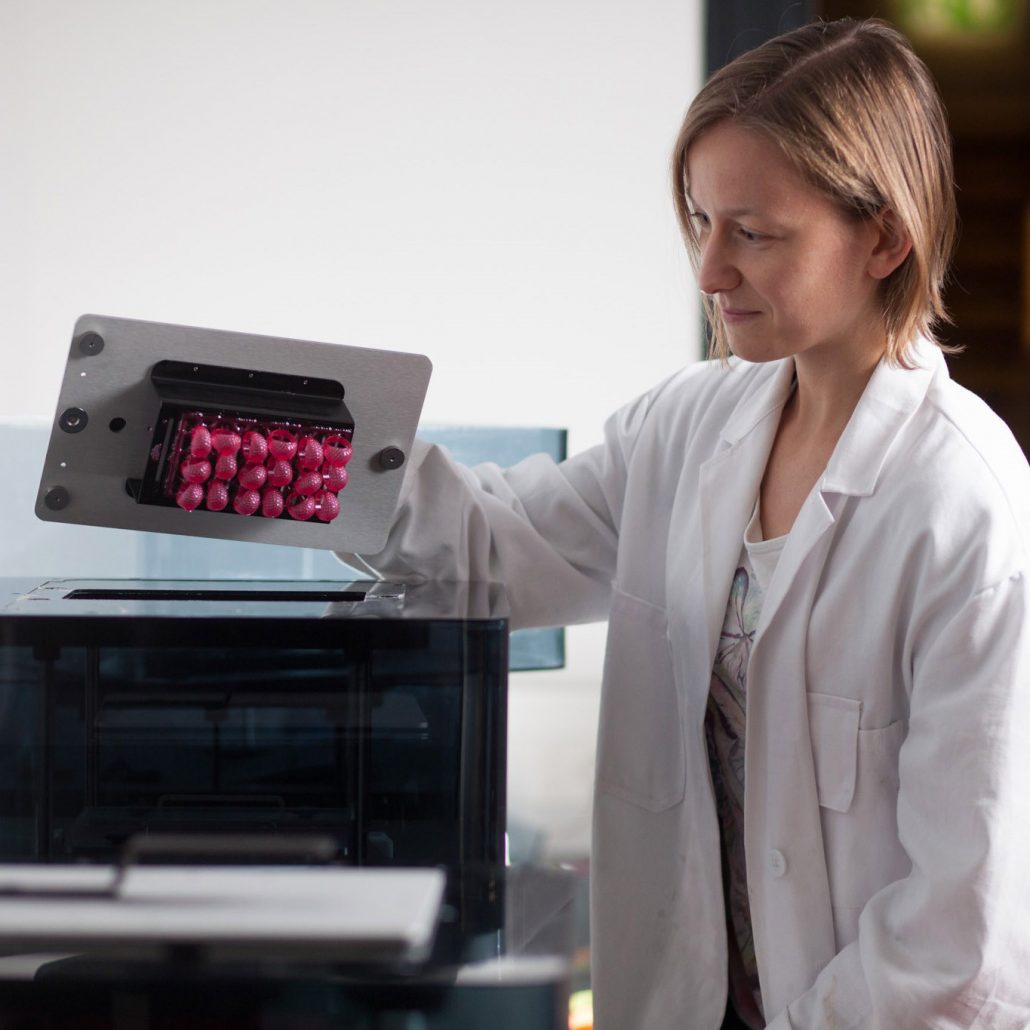
After having prepared the files for printing, they are sent to the 3D printer and the object is being printed layer by layer on the building platform of the printer. Once the object is printed, it has to be removed from the building platform.
Post-Processing
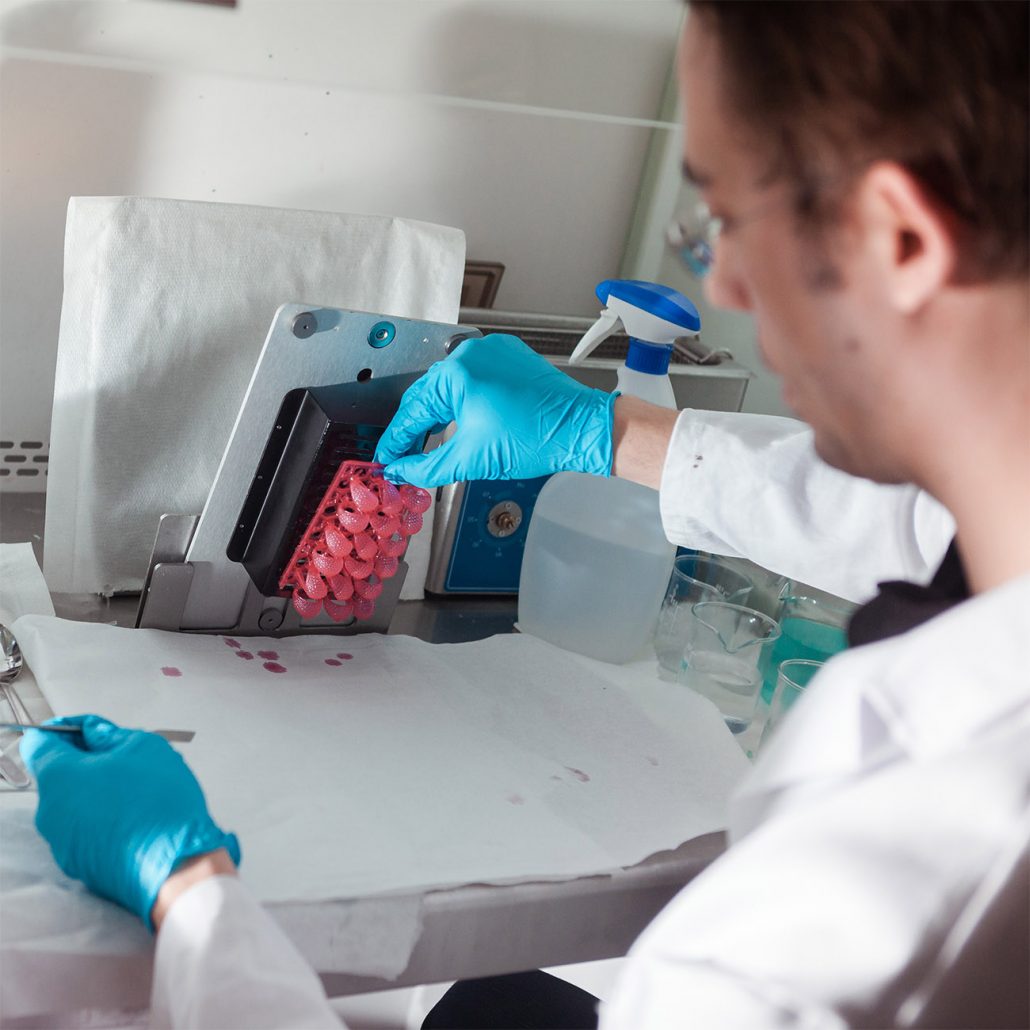
The printed object needs to be cleaned and cleared from support structures. Depending on the material, the parts also have to be post-cured in a flash device.
Watch the time lapse video showing the 3D printing process of dental splints:
Material
For DLP 3D prints, liquid photopolymers are used as printing materials.
The SolFlex 3D printers are designed to be open systems. They are tested to work with materials of all leading material manufacturers. A custom-designed UV light source allows our customers to use a broad range of materials, such as clear transparent materials, biocompatible, and filled materials. Establishing strong partnerships with major material suppliers ensures cutting-edge material technology, quick and easy access to the newest applications and constant material improvement.
Software
The software used in 3D printing is essential for the printing results. On the one hand, the software helps to prepare the objects for printing and on the other hand, it allows to navigate and monitor the printing process on the printer.
In terms of software, the SolFlex devices are compatible with most of the common slicing and nesting software packages such as Netfabb. A specially developed engine for Netfabb enables an intuitive positioning of 3D models as well as an automatic generation of minimally invasive support structures which results in reduced post-processing times.
The SolFlex family is characterized by the fact that all 3D printers are true standalone devices. Hence, print jobs can be started directly on the printer via a touch screen interface. After having created a print job, the file is transferred to the SolFlex 3D printer by using a network or USB port.
Hasnerstraße 123
1160 Vienna | Austria
Contact
+43 (0) 1 306 28 57
office@way2production.at




